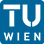- WS-BPEL Extension for People (BPEL4People), Version 1.0and
- Web Services Human Task (WS-HumanTask), Version 1.0
have been released by Active Endpoints, Adobe, BEA, IBM, Oracle and SAP on Monday, 25. June 2007. Consequently some syntax and interface proposal as listed on this site became obsolete that we want to integrate with the syntax via conceptional meta-models.
Abstract
The need for integration of human interaction scenarios into BPEL processes lead to the formalisation of tasks and human roles. The specifications BPEL4People and WS- HumanTask introduce, among other definitions, a dedicated people activity that uses a task performed by a human as well as human roles that describe the relationship of people, processes and tasks. This work presents the architecture of Vienna BPEL for People (VieBOP), a new BPEL4People system that can be coupled with an arbitrary BPEL engine. We evaluate the standards for BPEL4People and WS- HumanTask against goals as derived from the BPEL4People white paper and compare it to our work.
Problem Definition & Movtivation
Web services have become widely accepted as the de-facto standard for distributed business applications. They bring maximum interoperability, use an open and flexible architecture, and the implementation and complexity of a Web service can be hidden towards a service requestor. Layered on top of these services, BPEL, the standard for Web service orchestration, formally describes processes. While external activities correspond to Web services, human interactions and process activities that are related to human aspects cannot be specified using plain BPEL. Thus, while BPEL glues together the logic of a process, individual solutions have to be realised when people are integrated into business processes. Thus: there is a need to integrate people into BPEL processes.
Goals
Within the context of a business process BPEL4People must
- support role based interaction of people
- provide means of assigning users to generic human roles
- take care to delegate ownership of a task to a person only
- support scenario as
- four eyes scenario
- nomination
- escalation
- chained execution
by extending BPEL with additional independent syntax and semantic.
Syntax & Semantic
- WS-BPEL Extension for People (BPEL4People), Version 1.0 and
- Web Services Human Task (WS-HumanTask), Version 1.0
have been published by various companies.
System Interfaces
- additional XML Schemata and WSDL Interfaces for VieBOP
Architecture
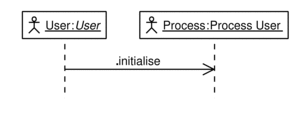
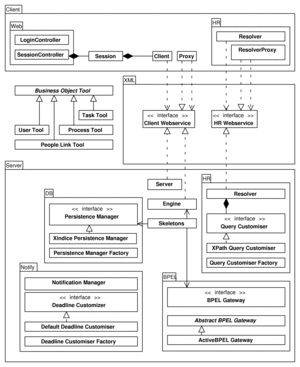
As BPEL4People really is an extension to BPEL, we chose to design a system that interacts with arbitrary BPEL engines while hosting BPEL4People information and managing BPEL processes on a people level. VieBOP thus encapsulates a traditional BPEL compliant engine transparently while offering specific interfaces to clients.
We can accomplish that by replacing BPEL extended elements into a set of invoke and receive activities for deployment on the BPEL engine. As with the people activity, the extension, that is hosted on VieBOP, then is transparently called by the BPEL engine.
Summary
Our syntax definition and our system:
- enables users to specify BPEL4People definitions
- by assigning people to roles
- by creating tasks for BPEL process activities, that are encapsulated by people activities
- by creating processes
- enables users to work with BPEL4People instances
- by instantiating processes
- by querying tasks and processes
- by altering a tasks state
- by submitting work and ad hoc attachments
- interacts proactively with users by notifying users of changes or events
- hosts people activities
- that encapsulate human tasks
- that are invokable transiently as common activities by BPEL processes and engines
- interacts with a BPEL engine
- by managing the people activities state and result within the context of the process
- by deploying a BPEL process to it, while extracting and conserving BPEL4People specific information, that will be associated with the process
Further Work
Demo
The source code of the early BPEL4People prototype has been released under the GPL and can be retrieved together with a thesis and a poster from SourceForges SVN repository
Publications
2008
- Holmes T., Tran H., Zdun U., Dustdar S.: Modeling Human Aspects of Business Processes - A View-Based, Model-Driven Approach. 4th European Conference on Model Driven Architecture Foundations and Applications, 2008, Page 247-262. April 2008. Download
- Holmes T., Vasko M., Dustdar S.: VieBOP: Extending BPEL Engines with BPEL4People. 16th Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and network-based Processing 2008, Page 547-555. February 2008. Download